Android location APIs make it easy for you to build location-aware
applications, without needing to focus on the details of the underlying
location technology. This becomes possible with the help of Google Play services,
which facilitates adding location awareness to your app with automated
location tracking, geofencing, and activity recognition.
This tutorial shows you how to use Location Services in your app to get the current location, get periodic location updates, look up addresses etc
The AsyncTask must be subclassed to be used and the subclass will override doInBackground(Params...) method to perform a task in the background and onPostExecute(Result) method is invoked on the UI thread after the background computation finishes and at the time to display the result. There is one more important method available in AyncTask which is execute(Params... params), this method executes the task with the specified parameters.
Check following example to have better understanding on how we use AynchTask in any Android application to get work done in the background without interfering main task.
3. Copy the library project at <android-sdk>/extras/google/google_play_services/libproject/google-play-services_lib/ to the location where you maintain your Android app projects. If you are using Eclipse, import the library project into your workspace. Click File > Import, select Android > Existing Android Code into Workspace, and browse to <android-sdk>/extras/google/google_play_services/libproject/, library project to import it.
Let's add Google Play Service reference in the project. Right click on the project and select Build Path > Configure Build Path > Android > and then click Add button which will show google-play-service_lib option to be added, just double click on it, which will add required library reference and you will have window as follows:
Following is the content of the modified main activity file src/com.example.lbsdemo/MainActivity.java.
 icon from the toolbar. Before starting your application, Eclipse will
display following window to select an option where you want to run your
Android application.
icon from the toolbar. Before starting your application, Eclipse will
display following window to select an option where you want to run your
Android application.
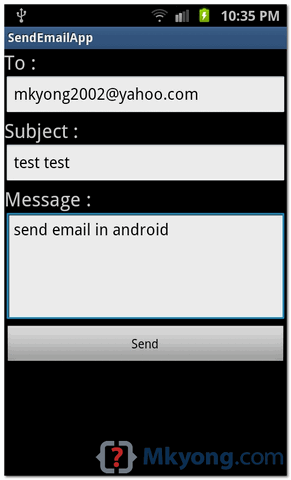
Select mobile device as an option and then check your mobile device which will display following screen:
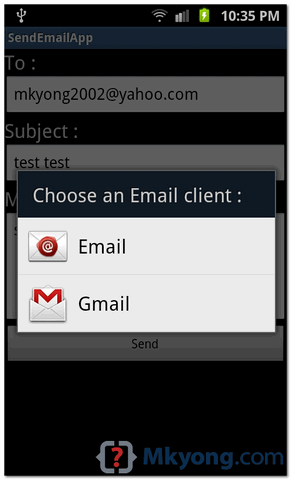
Now to see location select Get Location Button which will display location information as follows:
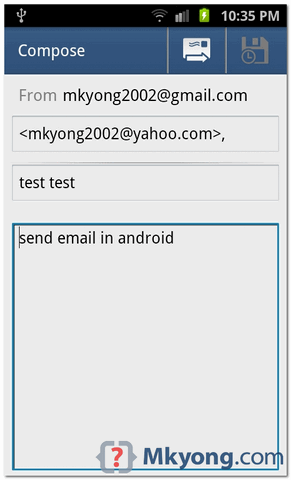
You can try by disconnecting location client using Disconnect Service and then connecting it by using Connect Service button. You can also modify to get location update as explained above and in Android Official documentation.
This tutorial shows you how to use Location Services in your app to get the current location, get periodic location updates, look up addresses etc
Get the Current Location
To get the current location, create a location client which is LocationClient object, connect it to Location Services using connect() method, and then call its getLastLocation() method. This method returns the most recent location in the form of Location object that contains latitude and longitude coordinates and other information as explained above. To have location based functionality in your activity, you will have to implement two interfaces:- GooglePlayServicesClient.ConnectionCallbacks
- GooglePlayServicesClient.OnConnectionFailedListener
Displaying a Location Address
Once you have Location object, you can use Geocoder.getFromLocation() method to get an address for a given latitude and longitude. This method is synchronous, and may take a long time to do its work, so you should call the method from the doInBackground() method of an AsyncTask class.The AsyncTask must be subclassed to be used and the subclass will override doInBackground(Params...) method to perform a task in the background and onPostExecute(Result) method is invoked on the UI thread after the background computation finishes and at the time to display the result. There is one more important method available in AyncTask which is execute(Params... params), this method executes the task with the specified parameters.
Check following example to have better understanding on how we use AynchTask in any Android application to get work done in the background without interfering main task.
Example :
Following example shows you in practical how to to use Location Services in your app to get the current location and its equivalent addresses etcInstall the Google Play Services SDK
Before you proceed to have location support in your Android Applications, you neet to setup Google Play Services SDK using following simple steps- Launch the SDK Manager.
- From Eclipse (with ADT), select Window > Android SDK Manager.
- On Windows, double-click the SDK Manager.exe file at the root of the Android SDK directory.
- On Mac or Linux, open a terminal and navigate to the tools/ directory in the Android SDK directory, then execute android sdk.
3. Copy the library project at <android-sdk>/extras/google/google_play_services/libproject/google-play-services_lib/ to the location where you maintain your Android app projects. If you are using Eclipse, import the library project into your workspace. Click File > Import, select Android > Existing Android Code into Workspace, and browse to <android-sdk>/extras/google/google_play_services/libproject/, library project to import it.
Create Android Application:
| 1 | You will use Eclipse IDE to create an Android application and name it as LBSDemo/i> under a package com.example.lbsdemo. While creating this project, make sure you Target SDK and Compile With at the latest version of Android SDK to use higher levels of APIs. | |||
| 2 | Add Google Play Service library in your project by following simple steps given below. | |||
| 3 | Modify src/MainActivity.java file and add required code as shown below to take care of getting current location and its equivalent address. | |||
| 4 | Modify layout XML file res/layout/activity_main.xml to add all GUI components which include three buttons and two text views to show location/address. | |||
| 5 | Modify res/values/strings.xml to define required constant values | |||
| 6 | Modify AndroidManifest.xml as shown below | |||
| 7 | Run the application to launch Android emulator and verify the result of the changes done in the aplication. |
Let's add Google Play Service reference in the project. Right click on the project and select Build Path > Configure Build Path > Android > and then click Add button which will show google-play-service_lib option to be added, just double click on it, which will add required library reference and you will have window as follows:
package com.example.lbsdemo;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Locale;
import com.google.android.gms.common.ConnectionResult;
import com.google.android.gms.common.GooglePlayServicesClient;
import com.google.android.gms.location.LocationClient;
import android.content.Context;
import android.location.Address;
import android.location.Geocoder;
import android.location.Location;
import android.os.AsyncTask;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v4.app.FragmentActivity;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.TextView;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class MainActivity extends FragmentActivity implements
GooglePlayServicesClient.ConnectionCallbacks,
GooglePlayServicesClient.OnConnectionFailedListener
{
LocationClient mLocationClient;
private TextView addressLabel;
private TextView locationLabel;
private Button getLocationBtn;
private Button disconnectBtn;
private Button connectBtn;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
locationLabel = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.locationLabel);
addressLabel = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.addressLabel);
getLocationBtn = (Button) findViewById(R.id.getLocation);
getLocationBtn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(View view) {
displayCurrentLocation();
}
});
disconnectBtn = (Button) findViewById(R.id.disconnect);
disconnectBtn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(View view) {
mLocationClient.disconnect();
locationLabel.setText("Got disconnected....");
}
});
connectBtn = (Button) findViewById(R.id.connect);
connectBtn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(View view) {
mLocationClient.connect();
locationLabel.setText("Got connected....");
}
});
// Create the LocationRequest object
mLocationClient = new LocationClient(this, this, this);
}
@Override
protected void onStart() {
super.onStart();
// Connect the client.
mLocationClient.connect();
locationLabel.setText("Got connected....");
}
@Override
protected void onStop() {
// Disconnect the client.
mLocationClient.disconnect();
super.onStop();
locationLabel.setText("Got disconnected....");
}
@Override
public void onConnected(Bundle dataBundle) {
// Display the connection status
Toast.makeText(this, "Connected", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
@Override
public void onDisconnected() {
// Display the connection status
Toast.makeText(this, "Disconnected. Please re-connect.",
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
@Override
public void onConnectionFailed(ConnectionResult connectionResult) {
// Display the error code on failure
Toast.makeText(this, "Connection Failure : " +
connectionResult.getErrorCode(),
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
public void displayCurrentLocation() {
// Get the current location's latitude & longitude
Location currentLocation = mLocationClient.getLastLocation();
String msg = "Current Location: " +
Double.toString(currentLocation.getLatitude()) + "," +
Double.toString(currentLocation.getLongitude());
// Display the current location in the UI
locationLabel.setText(msg);
// To display the current address in the UI
(new GetAddressTask(this)).execute(currentLocation);
}
/*
* Following is a subclass of AsyncTask which has been used to get
* address corresponding to the given latitude & longitude.
*/
private class GetAddressTask extends AsyncTask<Location, Void, String>{
Context mContext;
public GetAddressTask(Context context) {
super();
mContext = context;
}
/*
* When the task finishes, onPostExecute() displays the address.
*/
@Override
protected void onPostExecute(String address) {
// Display the current address in the UI
addressLabel.setText(address);
}
@Override
protected String doInBackground(Location... params) {
Geocoder geocoder =
new Geocoder(mContext, Locale.getDefault());
// Get the current location from the input parameter list
Location loc = params[0];
// Create a list to contain the result address
List<Address> addresses = null;
try {
addresses = geocoder.getFromLocation(loc.getLatitude(),
loc.getLongitude(), 1);
} catch (IOException e1) {
Log.e("LocationSampleActivity",
"IO Exception in getFromLocation()");
e1.printStackTrace();
return ("IO Exception trying to get address");
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e2) {
// Error message to post in the log
String errorString = "Illegal arguments " +
Double.toString(loc.getLatitude()) +
" , " +
Double.toString(loc.getLongitude()) +
" passed to address service";
Log.e("LocationSampleActivity", errorString);
e2.printStackTrace();
return errorString;
}
// If the reverse geocode returned an address
if (addresses != null && addresses.size() > 0) {
// Get the first address
Address address = addresses.get(0);
/*
* Format the first line of address (if available),
* city, and country name.
*/
String addressText = String.format(
"%s, %s, %s",
// If there's a street address, add it
address.getMaxAddressLineIndex() > 0 ?
address.getAddressLine(0) : "",
// Locality is usually a city
address.getLocality(),
// The country of the address
address.getCountryName());
// Return the text
return addressText;
} else {
return "No address found";
}
}
}// AsyncTask class
}
Following will be the content of res/layout/activity_main.xml file:<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<Button android:id="@+id/getLocation"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/get_location"/>
<Button android:id="@+id/disconnect"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/disconnect"/>
<Button android:id="@+id/connect"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/connect"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/locationLabel"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/addressLabel"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
</LinearLayout>
Following will be the content of res/values/strings.xml to define two new constants:<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<string name="app_name">LBSDemo</string>
<string name="action_settings">Settings</string>
<string name="hello_world">Hello world!</string>
<string name="get_location">Get Location</string>
<string name="disconnect">Disconnect Service</string>
<string name="connect">Connect Service</string>
</resources>
Following is the default content of AndroidManifest.xml:<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.example.lbsdemo"
android:versionCode="1"
android:versionName="1.0" >
<uses-sdk
android:minSdkVersion="8"
android:targetSdkVersion="17" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION"/>
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme" >
<activity
android:name="com.example.lbsdemo.MainActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application>
</manifest>
Let's try to run your LBSDemo application. I assume you have
connected your actual Android Mobile device with your computer. To run
the app from Eclipse, open one of your project's activity files and
click Run  icon from the toolbar. Before starting your application, Eclipse will
display following window to select an option where you want to run your
Android application.
icon from the toolbar. Before starting your application, Eclipse will
display following window to select an option where you want to run your
Android application.Select mobile device as an option and then check your mobile device which will display following screen:
Now to see location select Get Location Button which will display location information as follows:
You can try by disconnecting location client using Disconnect Service and then connecting it by using Connect Service button. You can also modify to get location update as explained above and in Android Official documentation.